Cocktail Installation to AWS on mac,linux
The procedure for installing Cocktail on Amazon Web Services Cloud is as follows.
Preparations
The following programs must be installed before installing Cocktail. Otherwise, an error will occur.
1) Set the environment variable path so that the provided Cube binary can be used in any directory.
2) Download and install Docker
https://store.docker.com/editions/community/docker-ce-desktop-windows
3) To install on AWS, access and secret keys must be added as environment variables.
- The account ID is the string contained in User ARN under IAM > Users > Summary.

To obtain the access and secret keys, click Security Credentials from the drop-down menu in the top-right corner of the AWS console.
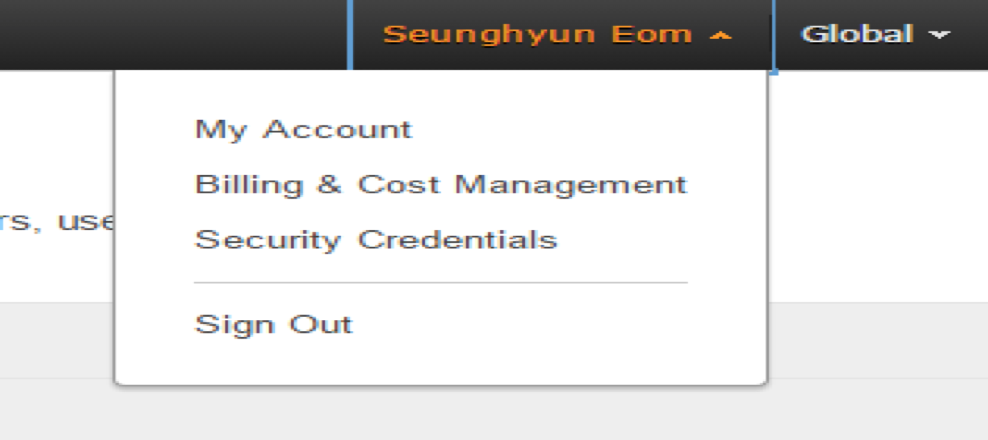
On the initial screen, you will be prompted with a warning message about creating IAM users. Continue by clicking the [Continue to Security Credentials] button on the left.
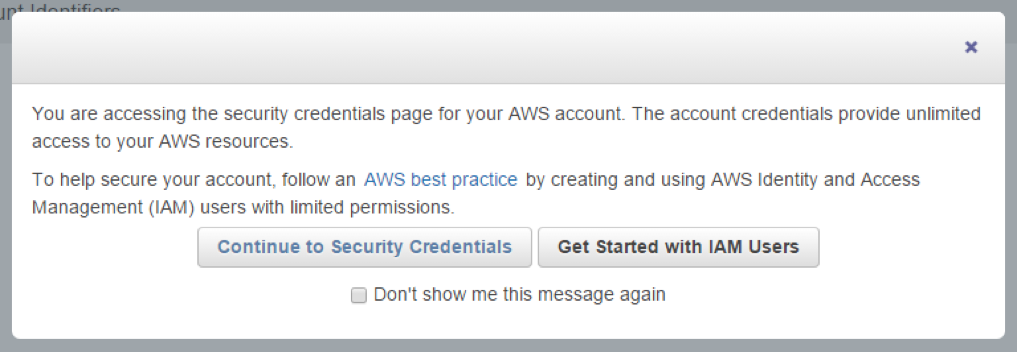
On the following screen, select [Access Keys (Access Key ID and Secret Access Key)] and click [Create New Access Key] to be issued new keys.
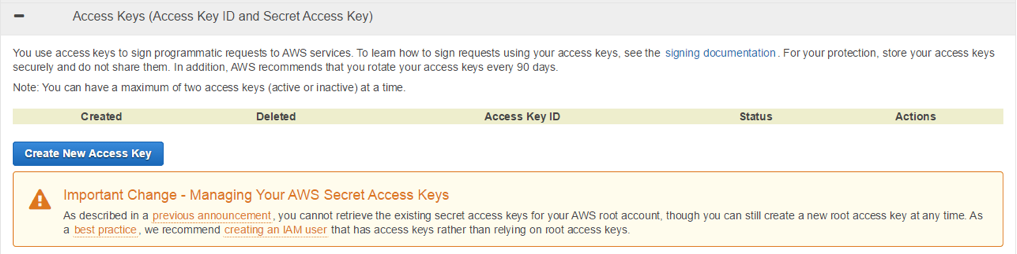
You will see the following screen when completed, and you will be able to check the Access Key and Credit Key via [Show Access Key]. You may also save the keys by clicking [Download Key File].
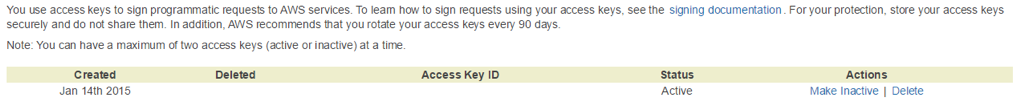
Register the values in the environment variables as shown below.
# export AWS_ACCOUNT_ID=xxxxxx
# export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=yyyyyy
# export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=zzzzzz
Installation
1. Create an empty directory for installation and move to that directory
# mkdir /Desktop/aws
# cd /Desktop/aws
2. Use the cube command to download and initialize the aws installation script.
# cube init -p aws
3. Open the cube.yam file with an editor and enter the information of the VM to be installed. Below is an example of a 1-master and 2-worker configuration.
---
cloud_provider: "aws"
# (optional) Instance size for the master node(s). Default: t2.medium.
master_vm_size: "t2.xlarge"
# (optional) Instance size for the worker node(s). Default: t2.medium.
worker_vm_size: "t2.medium"
# (required) The number of master nodes to be created. Example: 2
master_node_count: 1
# (required) The number of worker nodes to be created. Example: 3
worker_node_count: 2
# Just for reference.
# In order to retrieve regions and availability zone within the specific region use following commands
# aws configure
# aws ec2 describe-regions
# aws ec2 describe-availability-zones --region region-name
# region-code region-name Availability-Zone
# us-east-1 Virginia us-east-1a, us-east-1b, us-east-1c, us-east-1d, us-east-1e, us-east-1f
# us-west-2 Oregon us-west-2a, us-west-2b, us-west-2c
# us-west-1 N. California us-west-1b, us-west-1c
# eu-west-1 Ireland eu-west-1a, eu-west-1b, eu-west-1c
# eu-central-1 Frankfurt eu-central-1a, eu-central-1b, eu-central-1c
# ap-southeast-1 Singapore ap-southeast-1a, ap-southeast-1b
# ap-southeast-2 Sydney ap-southeast-2a, ap-southeast-2b, ap-southeast-2c
# ap-northeast-1 Tokyo ap-northeast-1a, ap-northeast-1c
# ap-northeast-2 Seoul ap-northeast-2a, ap-northeast-2c
# sa-east-1 Sao Paulo sa-east-1a, sa-east-1c
# ap-south-1 India (Mumbai) ap-south-1a, ap-south-1b
# (required) The region code.
region: "us-west-2"
# (required) The Availability Zone. It must be belong to region
azone: "us-west-2a"
# (required) Absolute Path to an SSH private key file to access server.
private_key_path: "/path/to/ssh_private_key"
# (required) Absolute Path to an SSH public key file to be provisioned as the SSH key.
key_path: "/path/to/ssh_public_key"
# Kubernetes
k8s_version: "1.9.8"
cluster_name: "cube"
domain_name: "acornsoft.io"
addons:
cm: false # cocktail + prometheus monitoring(without grafana)
km: false # kube dashboard + prometheus monitoring(with grafana)
# Prometheus Rule Language - en, ko, jp
alertmsg_lang: "en"
# (required) The unique cluster id. Equal or less than 50 characters.
cluster_id: "cluster_1234567896"
As shown above, private_key_path and key_path are private and public SSH key paths, respectively, for accessing servers and require the corresponding paths to be entered. If the keys already exist, simply enter the corresponding paths. To generate new keys, follow the procedure below.
< Generating New SSH Keys >
ㅤRefer to "Create and add private & public SSH keys" section in Overview
4. Install Cocktail on actual VM using the cube create command
# cube create
5. If the installation completes without errors, access the master device via SSH and verify that the containers that constitute cocktail-system is running normally.
# ssh -i ~/cube/pki/id_rsa root@{master1_ip}
# watch -n1 "kubectl get pods -n cocktail-system"
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
apollomq-3231363346-77ltx 1/1 Running 0 2m
cocktail-api-67592375-63k43 1/1 Running 1 2m
cocktail-client-4046445963-rrwhh 2/2 Running 1 2m
cocktail-cmdb-520687312-rhm8s 1/1 Running 0 2m
cocktail-metering-aws-3487533297-tw1x7 1/1 Running 0 2m
redis-3766055555-1lzmh 1/1 Running 0 2m
6. Check Cocktail Cloud access URL.
You can verify the Cocktail website URL and port using the following command.
# kubectl get service -n cocktail-system -o wide | grep cocktail-client-loadbalancer
Delete
1. Deletion is performed via the below command.
If an option is not provided by default, only generated k8s clusters are deleted and installation scripts remain intact. If the -f option is added, however, generated AWS infrastructures are deleted and installation scripts are also deleted after creating a backup of the cube.yaml file to cube.yaml.org.
Therefore, this command must be run with caution.
# cd /Desktop/cubetest
// Deletes k8s-generated persistent volumes and load balancers first.
// Deleted items must be verified via AWS console.
# cube destroy --pre-destroy
// Only deletes k8s and keeps installation scripts intact
# cube destroy
// Deletes k8s and installation scripts and backs up cube.yaml to cube.yaml.org.
# cube destroy -f
To reinstall after deleting, download the installation scripts again via the cube init command and reinstall.